Although some use the word “indexation” to indicate any aspect of technical search engine optimization (SEO), indexation is only part of the picture. Before you can get indexed, you have to get crawled. And you can’t rank in organic search results unless both have occurred.
Understanding the differences between each of these actions will help you manage your SEO channel more effectively.
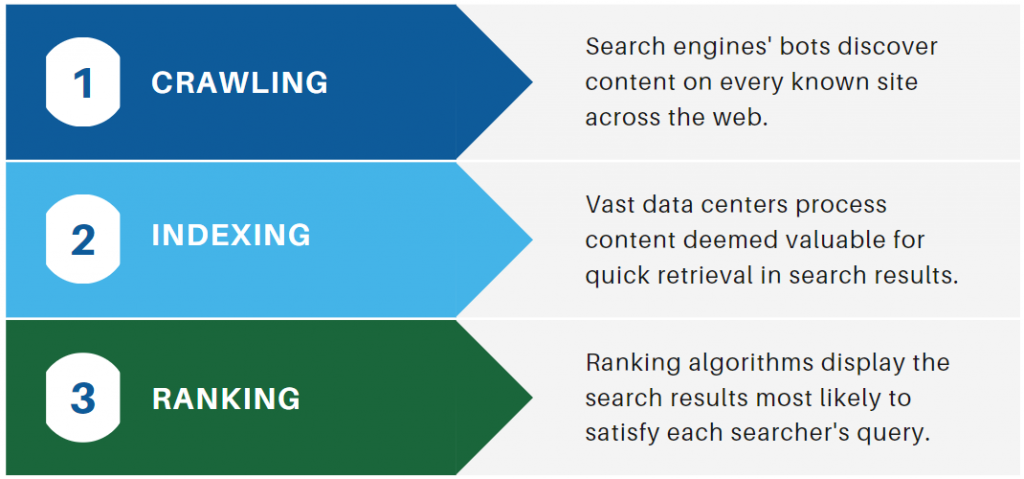
What Does Crawling Mean in SEO?
Everything SEO starts with the crawl — the process by which search engines discover the content on a site. Search engines send armies of bots — also known as crawlers or spiders — to every known website on the internet. When a bot reaches an active web page, it records the content and sends it home to one of the search engine’s many data centers for analysis. Then it uses one of the links on the page to access another page either on the same site or on another site altogether.
By crawling links in this manner, search engines have recorded trillions of pages of content, and located many trillions more.
Because the web changes ceaselessly, the cycle of crawling links and sending data home never ends. Over time, bots recrawl pages so that the most recent copy can be sent to replace the data center’s existing information. Many sites — such as large ecommerce and news sites — are crawled multiple times each day to ensure that the data center holds the most current content possible.
Not all sites are fully crawlable, depending on the decisions made in the site’s design and development. For instance, coding a link using a span tag as opposed to an anchor tag will render it uncrawlable for the bots. That link is essentially a locked door, hiding all of the content being linked to behind it. If there’s not another path to that content, it will never be eligible to rank in search results — it simply doesn’t exist in the eyes of the search engine.
What Does Indexing Mean in SEO?
When the data center receives a page of content from a bot, it analyzes the contextual relevance and stores it accordingly in its database. Thanks to this index of content, the search engine can instantly serve up results relevant to a search for a bass fish vs a bass musical clef or the Bass clothing brand.
However, indexation cannot occur without the crawl, which feeds the database the content to index.
What Does Ranking Mean in SEO?
The concept of SEO ranking seems self-explanatory, but it involves an unbelievably vast amount of data whizzing through a remarkably complex algorithm.
Search engines are essentially computer software that utilize sophisticated mathematical equations called algorithms to determine which content in the index is uniquely relevant to every single search query entered by each individual searcher. Rankings vary from second to second based on the information that the search engine has indexed about the person executing the search.
Ranking elements — the pieces that make up the algorithms — include information such as the context of the words on the page, the design of the page itself, and the speed with which the page loaded. In addition, information about the searcher — where they are, what they’ve searched for in the past, what they’ve clicked on in the past, and how engaging they found that content to be — is fed into the algorithms and affects the search results as well.
All pieces of the SEO puzzle must be in place to manage your optimization efforts effectively. The all-important rankings that most businesses desire cannot occur without the crawl and indexation pieces of the process. Without them, there would be nothing to return in the search results — which would make for a very sparse internet landscape.




